Absolute monarchy is a form of government where one person, typically a king or queen, holds complete control and power over the government and citizens. This system has been practiced throughout history, with some countries still maintaining elements of absolute monarchy today. To understand the complexities of absolute monarchy, it's essential to delve into its history, characteristics, and implications.
Historical Context of Absolute Monarchy
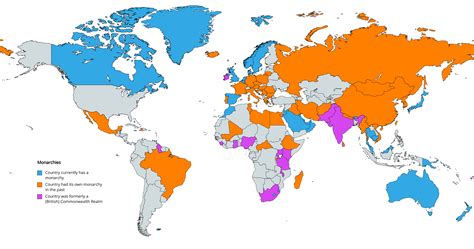
Absolute monarchy has its roots in ancient civilizations, where monarchs were often seen as divine rulers. The concept evolved over time, with the monarch’s power becoming more centralized and absolute. In Europe, the 16th to 18th centuries saw the rise of absolute monarchies, with notable examples including the reign of Louis XIV of France and Peter the Great of Russia. These monarchs consolidated power, reduced the influence of nobility, and established strong centralized governments.
Characteristics of Absolute Monarchy
An absolute monarchy is characterized by the monarch’s complete control over the government, laws, and citizens. Key features include the monarch’s absolute authority, lack of constitutional limits, and often, the absence of democratic institutions. The monarch may also hold significant influence over the economy, military, and social institutions. In some cases, absolute monarchies have been associated with authoritarianism, where the ruler’s power is maintained through repression and control.
| Characteristics | Description |
|---|---|
| Absolute Authority | The monarch holds complete control over the government and citizens. |
| Lack of Constitutional Limits | There are no formal checks on the monarch's power. |
| Centralized Government | Decision-making authority is concentrated in the monarch's hands. |
| Economic Control | The monarch may hold significant influence over the economy and resources. |
| Social Influence | The monarch may shape social institutions and cultural norms. |

Examples of Absolute Monarchies
Today, a few countries still maintain absolute monarchies, including Saudi Arabia, Brunei, and Oman. These monarchies have adapted to modern times, with some incorporating elements of constitutional monarchy or democratic institutions. However, the monarch’s power remains significant, and the systems are often characterized by a lack of transparency and accountability.
Implications of Absolute Monarchy
The implications of absolute monarchy are far-reaching, with potential consequences for human rights, economic development, and social stability. Critics argue that absolute monarchies can lead to repression, corruption, and inequality, while supporters claim that a strong, centralized government can provide stability and security. Ultimately, the success of an absolute monarchy depends on the monarch’s leadership, the country’s institutions, and the balance of power between the ruler and citizens.
Key Points
- Absolute monarchy is a system of government where one person holds complete control and power.
- The concept has evolved over time, with historical examples including ancient civilizations and European monarchies.
- Characteristics of absolute monarchy include absolute authority, lack of constitutional limits, and centralized government.
- Examples of absolute monarchies today include Saudi Arabia, Brunei, and Oman.
- The implications of absolute monarchy are complex, with potential consequences for human rights, economic development, and social stability.
Absolute monarchy is a complex and multifaceted system of government, with a rich history and varied implications. While some argue that absolute monarchy can provide stability and efficiency, others criticize its lack of accountability and potential for abuse of power. As the world continues to evolve, it's essential to understand the characteristics, examples, and implications of absolute monarchy, and to consider the trade-offs between different systems of government.
What is the main characteristic of an absolute monarchy?
+The main characteristic of an absolute monarchy is the monarch's complete control and power over the government and citizens, with no formal checks or limits on their authority.
Which countries still maintain absolute monarchies today?
+A few countries that still maintain absolute monarchies today include Saudi Arabia, Brunei, and Oman. These monarchies have adapted to modern times, but the monarch's power remains significant.
What are the potential implications of absolute monarchy?
+The potential implications of absolute monarchy are complex and far-reaching, with possible consequences for human rights, economic development, and social stability. Critics argue that absolute monarchies can lead to repression, corruption, and inequality, while supporters claim that a strong, centralized government can provide stability and security.
Meta description: “Discover the characteristics, examples, and implications of absolute monarchy, a system of government where one person holds complete control and power.” (150 characters)