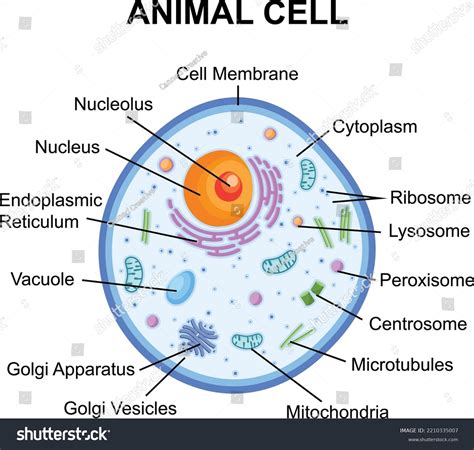
The animal cell is a complex and fascinating structure that is composed of several distinct parts, each with its own unique function and characteristics. Understanding the different components of an animal cell is essential for grasping the basics of biology and appreciating the intricate mechanisms that govern life. In this article, we will delve into the 5 main parts of an animal cell, exploring their roles, structures, and importance in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Key Points
- The cell membrane is the outermost layer of the cell, regulating the movement of materials in and out.
- The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance inside the cell, where many metabolic processes take place.
- The nucleus is the control center of the cell, containing most of the cell's genetic material.
- Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, generating energy through cellular respiration.
- The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranous tubules and cisternae, involved in protein synthesis and transport.
Nucleus: The Control Center

The nucleus is the largest organelle in an animal cell and is often referred to as the control center. It contains most of the cell’s genetic material, or DNA, which is organized into structures called chromosomes. The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which regulates the movement of materials in and out of the nucleus. The nucleus plays a critical role in cellular functions such as growth, reproduction, and metabolism, and is essential for the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.
Structure and Function of the Nucleus
The nucleus is composed of several distinct regions, including the nucleoplasm, chromatin, and nucleolus. The nucleoplasm is the gel-like substance inside the nucleus, where the chromatin is suspended. Chromatin is the complex of DNA and proteins that makes up the chromosomes, and is responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information. The nucleolus is a region within the nucleus where ribosome synthesis occurs, and is often visible as a distinct structure under a microscope.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Nuclear Envelope | Regulates movement of materials in and out of nucleus |
| Nucleoplasm | Supports chromatin and regulates nuclear processes |
| Chromatin | Stores and transmits genetic information |
| Nucleolus | Synthesizes ribosomes |
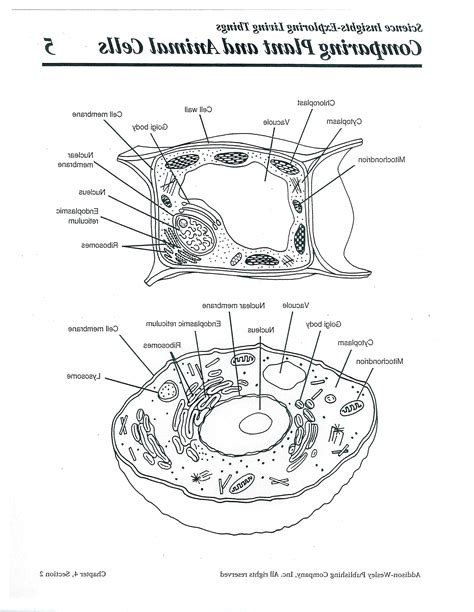
Mitochondria: The Powerhouses
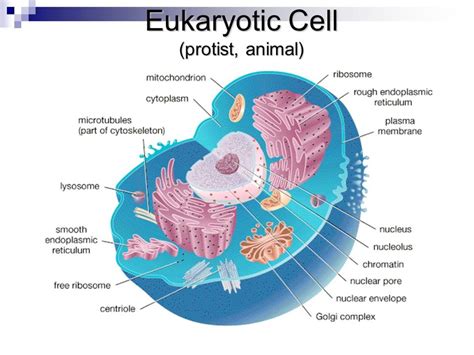
Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell, due to their critical role in generating energy through cellular respiration. Mitochondria are organelles that are found in the cytoplasm of animal cells, and are responsible for producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the primary energy currency of the cell. Mitochondria have a unique structure, with an outer membrane and an inner membrane that is folded into a series of cristae. This folded structure increases the surface area of the mitochondria, allowing for more efficient energy production.
Structure and Function of Mitochondria
Mitochondria are composed of several distinct regions, including the outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, and matrix. The outer membrane is permeable, allowing certain substances to pass through, while the inner membrane is impermeable and folded into cristae. The intermembrane space is the region between the outer and inner membranes, and the matrix is the gel-like substance inside the mitochondria where the citric acid cycle and fatty acid oxidation take place.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Outer Membrane | Permeable, allows certain substances to pass through |
| Inner Membrane | Impermeable, folded into cristae to increase surface area |
| Intermembrane Space | Region between outer and inner membranes |
| Matrix | Site of citric acid cycle and fatty acid oxidation |
Endoplasmic Reticulum: The Network
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranous tubules and cisternae that is found in the cytoplasm of animal cells. The ER is involved in several critical cellular processes, including protein synthesis, transport, and modification. The ER is composed of two distinct regions, the rough ER and the smooth ER, which are distinguished by the presence or absence of ribosomes on their surface.
Structure and Function of the Endoplasmic Reticulum
The rough ER is studded with ribosomes, which are responsible for synthesizing proteins that are destined for secretion or insertion into cellular membranes. The smooth ER, on the other hand, is involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification. The ER is also responsible for transporting proteins and lipids throughout the cell, and plays a critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Rough ER | Involved in protein synthesis, transport, and modification |
| Smooth ER | Involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification |
| ER Lumen | Site of protein folding and modification |
Cytoplasm: The Jelly-Like Substance
The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance that fills the cell and surrounds the organelles. It is composed of a mixture of water, salts, sugars, and various organic molecules, and provides a medium for chemical reactions to occur. The cytoplasm is also home to many metabolic processes, including glycolysis, which is the first step in cellular respiration.
Structure and Function of the Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is composed of several distinct regions, including the cytosol, which is the liquid portion of the cytoplasm, and the cytoskeleton, which is a network of protein filaments that provides structural support and shape to the cell. The cytoplasm is also home to many organelles, including mitochondria, which are responsible for generating energy, and ribosomes, which are responsible for protein synthesis.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Cytosol | Provides medium for chemical reactions to occur |
| Cytoskeleton | Provides structural support and shape to the cell |
| Organelles | Perform various cellular functions, such as energy production and protein synthesis |
Cell Membrane: The Outermost Layer
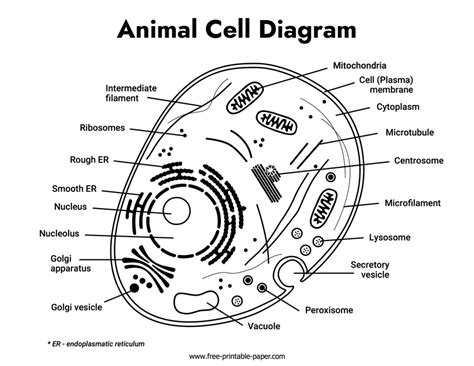
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is the outermost layer of the cell and is responsible for regulating the movement of materials in and out of the cell. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, with embedded proteins that perform various functions, such as transport, signaling, and cell-cell recognition. The cell membrane is semi-permeable, allowing certain substances to pass through while keeping others out.
Structure and Function of the Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is composed of several distinct regions, including the phospholipid bilayer, which is the main structural component of the membrane, and the embedded proteins, which perform various functions. The cell membrane is also home to many receptors, which are responsible for recognizing and binding to specific molecules, such as hormones and neurotransmitters.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Phospholipid Bilayer | Provides main structural component of the membrane |
| Embedded Proteins | Perform various functions, such as transport, signaling, and cell-cell recognition |
| Receptors | Recognize and bind to specific molecules, such as hormones and neurotransmitters |
What is the main function of the nucleus in an animal cell?
+The main function of the nucleus is to store and transmit genetic information, and to regulate cellular processes such as growth, reproduction, and metabolism.
What is the role of mitochondria in cellular respiration?
+Mitochondria are the site of cellular respiration, where energy is generated through the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum in protein synthesis?
+The endoplasmic reticulum is involved in protein synthesis, transport, and modification, and is responsible for synthesizing proteins that are destined for secretion or insertion into cellular membranes.
Meta Description: Explore the 5 main parts of an animal cell, including the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, and cell membrane, and discover their roles and functions in maintaining cellular homeostasis.