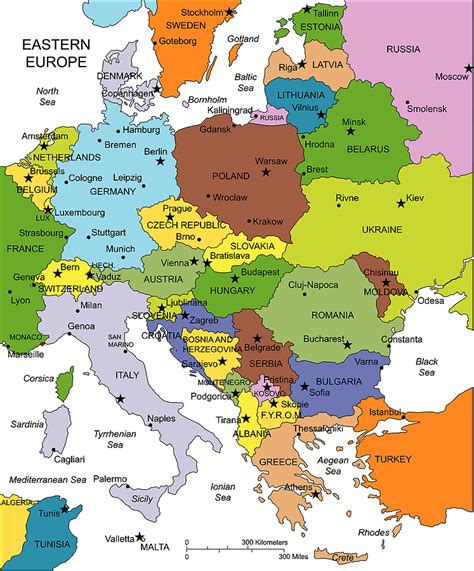
Eastern Europe, a region of immense cultural, historical, and geographical diversity, spans across a significant portion of the European continent. The area is bounded by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Ural Mountains to the east, the Black Sea and the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. This vast and varied region includes countries such as Poland, Russia, Ukraine, and many others, each with its unique history, language, and customs. Understanding Eastern Europe through maps can provide invaluable insights into its complex geography, political divisions, and the strategic importance of the region.
Geographical Overview of Eastern Europe
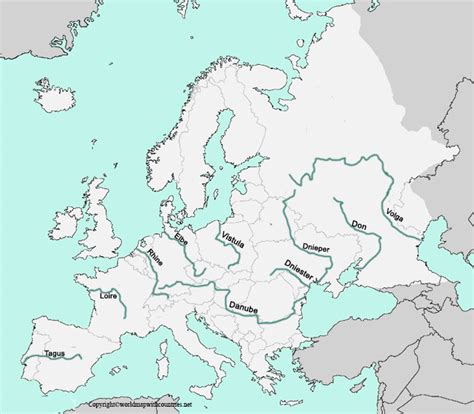
A geographical map of Eastern Europe reveals a landscape dominated by plains, with the exception of the Carpathian Mountains in the south and the Ural Mountains in the east. The region is drained by several major rivers, including the Volga, the Danube, and the Dnieper, which play crucial roles in the economy and ecology of the area. The climate varies significantly from north to south, ranging from subarctic to temperate and Mediterranean. This diversity in geography supports a wide range of flora and fauna, contributing to the region’s rich biodiversity.
Political Boundaries and Countries
A political map of Eastern Europe shows the complex mosaic of countries that make up the region. From the Baltic states of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania in the north, to Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, and Hungary in the central part, and down to Romania, Bulgaria, and the countries of the former Yugoslavia in the south, each nation has its own distinct political system, economy, and cultural heritage. Russia, the largest country in the world by land area, dominates the eastern part of the region, with Ukraine being another significant player in terms of size and strategic importance.
| Country | Capital City | Population (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Poland | Warsaw | 38 million |
| Russia | Moscow | 146 million |
| Ukraine | Kyiv | 41 million |
| Romania | Bucharest | 19 million |
| Bulgaria | Sofia | 7 million |

Economic Landscape of Eastern Europe

The economic map of Eastern Europe reveals a region of contrasts, with some countries experiencing rapid economic growth and integration into the global economy, while others face challenges related to transition from centrally planned to market-based economies. The region is rich in natural resources, including oil, natural gas, coal, and timber, which are significant contributors to the economies of countries like Russia and Poland. The agricultural sector is also important, with countries such as Ukraine being major exporters of grains. However, the economic development of the region is also influenced by its political stability, corruption levels, and the pace of reforms.
Historical Context and Evolution
A historical map of Eastern Europe would show a region that has been shaped by numerous empires, wars, and political ideologies throughout the centuries. From the Roman Empire to the Mongol invasions, the rise and fall of the Soviet Union, and the dissolution of Yugoslavia, each historical event has left its mark on the region’s political boundaries, cultural identity, and economic systems. Understanding this historical context is essential for grasping the complexities of the modern Eastern European landscape.
Key Points
- Eastern Europe is a region of significant geographical and cultural diversity.
- The region's political landscape is complex, with many countries having undergone significant changes in recent decades.
- Economically, the region is rich in natural resources and has the potential for substantial economic growth.
- Historical events have played a crucial role in shaping the region's current political, economic, and cultural landscape.
- Understanding Eastern Europe requires a deep dive into its geography, politics, economy, and history.
In conclusion, Eastern Europe is a multifaceted region that offers a unique blend of history, culture, and natural beauty. Through the lens of various maps, one can gain a deeper understanding of its geography, political divisions, economic potential, and historical context. As the region continues to evolve, both economically and politically, its significance on the global stage is likely to grow, making it an increasingly important area of study and exploration.
What are the main geographical features of Eastern Europe?
+Eastern Europe is characterized by vast plains, with the exception of the Carpathian Mountains in the south and the Ural Mountains in the east. Major rivers like the Volga, Danube, and Dnieper also play significant roles in the region’s geography.
Which countries are considered part of Eastern Europe?
+Eastern Europe includes countries such as Poland, Russia, Ukraine, Romania, Bulgaria, and the countries of the former Yugoslavia, among others. Each country has its unique cultural, historical, and economic characteristics.
What is the economic potential of Eastern Europe?
+The region is rich in natural resources, including oil, natural gas, and timber, and has significant agricultural potential. However, economic growth is influenced by factors such as political stability, corruption, and the pace of economic reforms.