The terms "fare" and "fair" are often confused with one another due to their similar spellings and pronunciations. However, these two words have distinct meanings and uses in the English language. Understanding the difference between "fare" and "fair" is essential for effective communication and to avoid confusion in various contexts. In this article, we will delve into the definitions, usage, and examples of both words to clarify their differences and provide a comprehensive understanding of their applications.
Key Points
- The word "fare" refers to the cost or price of something, especially transportation or food.
- The word "fair" can mean just, reasonable, or unbiased, and it can also refer to a gathering or festival.
- Using "fare" and "fair" correctly is crucial for clear and effective communication.
- Both words have multiple meanings and uses, and understanding their differences is essential for avoiding confusion.
- Practice and context are key to mastering the correct usage of "fare" and "fair".
Definition and Usage of “Fare”
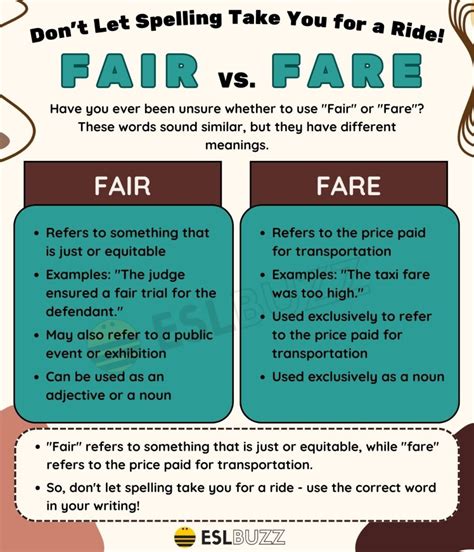
The word “fare” is primarily used to refer to the cost or price of something, especially in the context of transportation or food. For example, “The fare for the taxi ride was higher than expected” or “The restaurant’s fare was exquisite, but expensive.” In addition to its use in relation to cost, “fare” can also mean to perform or get along in a certain way, as in “She fared well in the competition” or “The company fared poorly in the economic downturn.” Understanding the different meanings of “fare” is essential to use the word correctly in various contexts.
Examples of “Fare” in Different Contexts
In the context of transportation, “fare” is commonly used to refer to the cost of a ticket or ride. For instance, “The fare for the subway is 3" or "The taxi fare from the airport to the city center is around 20.” In the context of food, “fare” can refer to the type of cuisine or the quality of the food, as in “The restaurant serves Italian fare” or “The fare at the buffet was impressive.” Furthermore, “fare” can also be used to describe how someone or something performs or gets along, as in “The team fared well in the tournament” or “The economy fared poorly due to the pandemic.”
| Context | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Transportation | The fare for the bus ride is $2. |
| Food | The restaurant's fare includes a variety of vegetarian options. |
| Performance | The company fared well in the market despite the economic downturn. |

Definition and Usage of “Fair”
The word “fair” has multiple meanings and uses, including referring to something that is just, reasonable, or unbiased. For example, “The judge tried to be fair in her decision” or “The price of the product is fair considering its quality.” Additionally, “fair” can refer to a gathering or festival, such as a fairground or a trade fair. Understanding the different meanings of “fair” is crucial to use the word correctly in various contexts and to avoid confusion with “fare.”
Examples of “Fair” in Different Contexts
In the context of justice or reasonableness, “fair” is commonly used to describe a situation or decision that is unbiased or equitable. For instance, “The fair treatment of all employees is essential in any organization” or “The fair price of the product is $10.” In the context of gatherings or festivals, “fair” can refer to a specific event or location, as in “The fair is coming to town next weekend” or “The fairgrounds are located on the outskirts of the city.” Furthermore, “fair” can also be used to describe the weather, as in “The fair weather made it a perfect day for the outing.”
Comparison and Contrast of “Fare” and “Fair”
While “fare” and “fair” are distinct words with different meanings, they can be confused with one another due to their similar spellings and pronunciations. However, understanding the differences between the two words is essential for clear and effective communication. In general, “fare” refers to the cost or price of something, while “fair” refers to something that is just, reasonable, or unbiased. By recognizing the different meanings and uses of “fare” and “fair,” individuals can use the words correctly in various contexts and avoid confusion.
Common Mistakes and Confusions
One of the most common mistakes when using “fare” and “fair” is to confuse the two words due to their similar spellings and pronunciations. For example, saying “The fair for the taxi ride was high” instead of “The fare for the taxi ride was high.” Another common mistake is to use “fare” when referring to a gathering or festival, as in “The fare is coming to town next weekend” instead of “The fair is coming to town next weekend.” By recognizing these common mistakes and confusions, individuals can take steps to use the words correctly and avoid confusion.
What is the main difference between "fare" and "fair"?
+The main difference between "fare" and "fair" is that "fare" refers to the cost or price of something, while "fair" refers to something that is just, reasonable, or unbiased.
How can I avoid confusing "fare" and "fair"?
+To avoid confusing "fare" and "fair," it's essential to understand the different meanings and uses of the words. Practice using the words in context, and pay attention to the spelling and pronunciation of each word.
What are some common mistakes when using "fare" and "fair"?
+Common mistakes when using "fare" and "fair" include confusing the two words due to their similar spellings and pronunciations, and using "fare" when referring to a gathering or festival.
In conclusion, understanding the difference between “fare” and “fair” is essential for effective communication and to avoid confusion in various contexts. By recognizing the different meanings and uses of the words, individuals can use them correctly and confidently. With practice and context, mastering the correct usage of “fare” and “fair” can become second nature, and individuals can communicate more effectively and avoid confusion.



