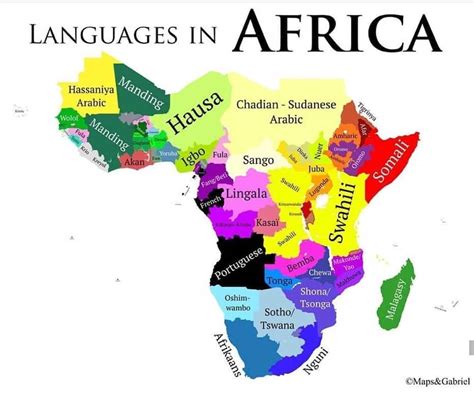
The African continent is home to a staggering array of languages, with estimates suggesting that there are over 2,000 languages spoken across its 55 countries. This linguistic diversity is a reflection of the continent's complex history, with various ethnic groups, empires, and colonial powers having shaped the language landscape over time. From the Afro-Asiatic languages spoken in the north, to the Niger-Congo languages spoken in the south, and the Khoisan languages spoken in the southeast, Africa's linguistic heritage is incredibly rich and varied.
Language Families in Africa

Africa’s languages can be broadly classified into several major language families, each with its own distinct characteristics and distribution. The Afro-Asiatic language family, which includes languages such as Arabic, Amharic, and Hausa, is spoken by approximately 300 million people across North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and parts of West Africa. The Niger-Congo language family, which includes languages such as Swahili, Yoruba, and Zulu, is spoken by around 500 million people across West, Central, and Southern Africa. The Khoisan language family, which includes languages such as San and Khoekhoe, is spoken by around 20,000 people in Southern Africa.
Afro-Asiatic Languages
The Afro-Asiatic language family is one of the oldest and most widely spoken language families in Africa. It is thought to have originated in the Middle East around 10,000 years ago, and from there it spread to North Africa and the Horn of Africa. Arabic, which is the most widely spoken Afro-Asiatic language, is the official language of many countries in North Africa and the Middle East. Other notable Afro-Asiatic languages include Amharic, which is the official language of Ethiopia, and Hausa, which is widely spoken in West Africa.
| Language | Speakers | Region |
|---|---|---|
| Arabic | 300 million | North Africa, Middle East |
| Amharic | 25 million | Horn of Africa |
| Hausa | 50 million | West Africa |

Niger-Congo Languages

The Niger-Congo language family is the largest language family in Africa, with over 1,500 languages spoken across West, Central, and Southern Africa. This language family is thought to have originated in West Africa around 5,000 years ago, and from there it spread to other parts of the continent. Swahili, which is the most widely spoken Niger-Congo language, is a lingua franca in East Africa and is spoken by around 100 million people. Other notable Niger-Congo languages include Yoruba, which is spoken in West Africa, and Zulu, which is spoken in Southern Africa.
Niger-Congo Language Subgroups
The Niger-Congo language family can be further divided into several subgroups, each with its own distinct characteristics and distribution. The Bantu subgroup, which includes languages such as Swahili, Zulu, and Shona, is spoken by around 200 million people across Central, East, and Southern Africa. The West African subgroup, which includes languages such as Yoruba, Igbo, and Wolof, is spoken by around 100 million people across West Africa.
Key Points
- Africa is home to over 2,000 languages, with the majority belonging to the Niger-Congo and Afro-Asiatic language families.
- The Afro-Asiatic language family is thought to have originated in the Middle East around 10,000 years ago.
- The Niger-Congo language family is the largest language family in Africa, with over 1,500 languages spoken across West, Central, and Southern Africa.
- Swahili is the most widely spoken Niger-Congo language, with around 100 million speakers across East Africa.
- The Bantu subgroup of the Niger-Congo language family is spoken by around 200 million people across Central, East, and Southern Africa.
Khoisan Languages
The Khoisan language family is a small but unique language family spoken by around 20,000 people in Southern Africa. This language family is thought to have originated in Southern Africa around 2,000 years ago, and is characterized by a distinctive system of clicks and consonants. The San language, which is spoken by the San people of Southern Africa, is one of the most well-known Khoisan languages.
Language Endangerment in Africa
Many languages in Africa are considered endangered, with some languages having as few as a few hundred speakers. The main factors contributing to language endangerment in Africa include urbanization, globalization, and the spread of dominant languages such as English and Arabic. Efforts are being made to document and preserve endangered languages, including language documentation projects and language education programs.
What is the most widely spoken language in Africa?
+Arabic is the most widely spoken language in Africa, with around 300 million speakers across North Africa and the Middle East.
What is the largest language family in Africa?
+The Niger-Congo language family is the largest language family in Africa, with over 1,500 languages spoken across West, Central, and Southern Africa.
What is the most endangered language family in Africa?
+The Khoisan language family is considered one of the most endangered language families in Africa, with around 20,000 speakers across Southern Africa.
In conclusion, the languages of Africa are incredibly diverse and complex, with a rich history and cultural significance. Understanding the language families and subgroups of Africa can help to promote language preservation and education, and to appreciate the unique cultural heritage of the continent. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, it is more important than ever to recognize and celebrate the linguistic diversity of Africa, and to work towards preserving the languages and cultures of this incredible continent.