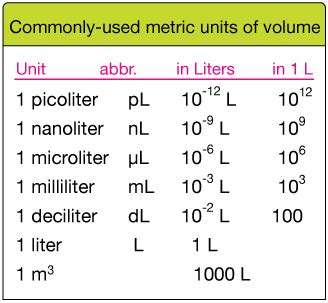
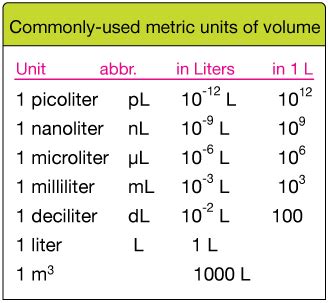
The relationship between milliliters (mL) and microliters (μL) is a fundamental concept in various scientific fields, including chemistry, biology, and medicine. Understanding this relationship is crucial for accurate measurements and calculations in laboratory settings and other applications. The key conversion factor to remember is that 1 milliliter (mL) is equal to 1000 microliters (μL). This conversion is based on the definition of these units within the International System of Units (SI), where 1 liter (L) equals 1000 milliliters (mL), and 1 milliliter (mL) equals 1000 microliters (μL).
Understanding the Basics of Volume Measurement

In the SI system, the liter (L) is the base unit of volume, with 1 liter being equal to 1000 milliliters. This makes the milliliter a commonly used unit for measuring volumes of liquids in scientific experiments and everyday applications. Further dividing the milliliter into smaller units leads to the microliter, which is one-thousandth of a milliliter. The microliter is particularly useful in microbiology, molecular biology, and other fields where very small volumes of liquids need to be measured with high precision.
Conversion Between mL and μL
Given that 1 mL equals 1000 μL, converting between these units is straightforward. To convert milliliters to microliters, you simply multiply the number of milliliters by 1000. Conversely, to convert microliters to milliliters, you divide the number of microliters by 1000. This conversion factor is essential for recipe scaling in cooking, dilution calculations in chemistry, and dosing calculations in pharmacology, among other applications.
| Volume in mL | Equivalent Volume in μL |
|---|---|
| 1 mL | 1000 μL |
| 0.5 mL | 500 μL |
| 0.1 mL | 100 μL |
Key Points
- 1 mL is equivalent to 1000 μL, providing a basic conversion factor for volume measurements.
- Conversions between mL and μL are crucial in scientific research, medical applications, and everyday measurements.
- Understanding these conversions enhances precision and accuracy in laboratory settings and beyond.
- Electronic and manual pipettes are essential tools for handling volumes in microliters, with careful handling required for accurate measurements.
- Applications of mL to μL conversions range from cooking and chemistry to microbiology and pharmacology.
Applications and Implications

The conversion between milliliters and microliters has far-reaching implications across various disciplines. In cooking, accurately scaling recipes requires converting between these units to ensure the right balance of ingredients. In scientific research, precise measurements are critical for the validity of experimental results. The conversion factor also plays a role in medical dosing, where the accurate administration of drugs is essential for patient safety and treatment efficacy.
Future Directions and Considerations
As technology advances, the precision and ease of volume measurements will continue to improve. Electronic pipettes and automated systems will become more prevalent, reducing human error and increasing the speed of laboratory workflows. However, understanding the fundamental relationships between units of volume, such as the equivalence of 1 mL to 1000 μL, will remain essential for professionals and researchers alike, ensuring that advancements in technology are leveraged effectively and safely.
How do I convert 2.5 mL to microliters?
+To convert 2.5 mL to microliters, multiply 2.5 by 1000, since 1 mL equals 1000 μL. Thus, 2.5 mL equals 2500 μL.
What is the importance of precise volume measurements in laboratory settings?
+Precise volume measurements are crucial in laboratory settings because they directly affect the accuracy and reliability of experimental results. Small discrepancies in measurements can lead to significant errors in conclusions, especially in fields like chemistry and pharmacology where reactions are highly sensitive to the quantities of reactants.
Can the conversion between mL and μL be applied in everyday situations?
+Yes, the conversion between mL and μL can be applied in various everyday situations, such as cooking, where recipes often require precise measurements of ingredients in milliliters or liters, and these may need to be adjusted or scaled up/down. Understanding the relationship between these units can help in making these adjustments accurately.
In conclusion, the relationship between milliliters and microliters, where 1 mL equals 1000 μL, is a fundamental principle that underlies many aspects of scientific and everyday measurements. Mastering this conversion is essential for professionals and individuals alike, facilitating accurate calculations, precise measurements, and informed decision-making across a wide range of applications.