Planting beans is a straightforward process that can be accomplished in various ways, depending on the type of bean, the climate, and the desired outcome. Beans are a versatile legume that can be grown in a wide range of conditions, from containers to large gardens. With their high protein content and ability to fix nitrogen in the soil, beans are a popular choice among gardeners. In this article, we will explore five different ways to plant beans, including traditional methods, innovative techniques, and space-saving strategies.
Key Points
- Direct sowing is a simple and effective way to plant beans in well-draining soil with a temperature above 60°F (15°C).
- Starting beans indoors 2-3 weeks before the last frost date can give them a head start on the growing season.
- Container gardening is ideal for small spaces, using a minimum of 6-8 hours of direct sunlight and a well-draining potting mix.
- Companion planting with beans and other vegetables, such as corn and squash, can improve growth and reduce pests.
- Hydroponic systems can provide a controlled environment for bean growth, with precise control over nutrient levels and pH.
Direct Sowing

Direct sowing is the most common method of planting beans. This involves sowing the seeds directly into the ground where they will grow. To direct sow beans, choose a location with well-draining soil and full sun. The soil temperature should be at least 60°F (15°C) for optimal germination. Sow the seeds 1-2 inches deep and 2-3 inches apart, depending on the variety. Water the soil gently but thoroughly, and keep the soil consistently moist during the first few weeks after planting. With proper care, beans can germinate within 7-10 days and be ready to harvest in as little as 50 days.
Preparation is Key
Before direct sowing, it’s essential to prepare the soil. Remove any debris, rocks, or weeds that could interfere with growth. If the soil is heavy clay or sandy, mix in some organic matter like compost or well-rotted manure to improve its structure. This will help the soil retain moisture, suppress weeds, and provide essential nutrients for the beans. A soil test can help determine the pH level and nutrient content, allowing for adjustments to be made before planting.
| Soil Type | pH Level | Nutrient Content |
|---|---|---|
| Clay | 6.0-7.0 | High in nutrients, but prone to waterlogging |
| Sandy | 6.0-7.0 | Low in nutrients, but well-draining |
| Loam | 6.0-7.0 | Balanced nutrient content, with good drainage |

Starting Indoors
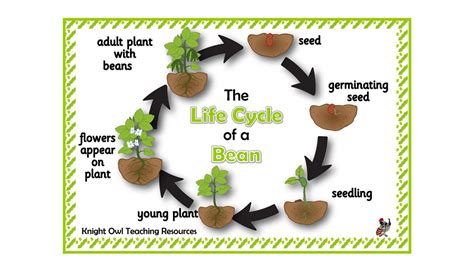
Starting beans indoors can give them a head start on the growing season. This method is particularly useful in areas with a short growing season or where the weather is unpredictable. To start beans indoors, fill a seed tray or small pots with a good quality seed starting mix. Sow the seeds about 1-2 inches deep and 1-2 inches apart. Place the tray or pots in a warm location, such as a sunny windowsill or under grow lights, with a consistent temperature of around 70-80°F (21-27°C). Keep the soil consistently moist, but not waterlogged. Once the seedlings have 2-3 sets of leaves, they can be transplanted outside, hardened off to acclimate to outdoor conditions.
Hardening Off
Hardening off is an essential step when starting beans indoors. This process involves gradually exposing the seedlings to outdoor conditions over the course of 7-10 days. Start by moving the seedlings to a shaded area outdoors, then gradually increase their exposure to direct sunlight and wind. This will help the seedlings develop a stronger stem and more robust root system, reducing the risk of transplant shock.
Container Gardening
Container gardening is a great way to grow beans in small spaces, such as balconies, patios, or rooftops. Choose a container that is at least 6-8 inches deep and has drainage holes to prevent waterlogging. Fill the container with a well-draining potting mix, and sow the seeds 1-2 inches deep and 2-3 inches apart. Place the container in a location that receives at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day. Water the soil consistently, but avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot. With proper care, beans can thrive in containers and be ready to harvest in as little as 50 days.
Supporting the Plants
Beans are climbing plants and will need support as they grow. Provide a trellis, stake, or other support system for the plants to climb on. This will help keep the plants upright, promote better growth, and make harvesting easier. For bush beans, a cage or stake can be used to keep the plants upright and encourage better fruiting.
Companion Planting
Companion planting involves growing different plants together to improve their growth and reduce pests. Beans are a popular choice for companion planting, as they fix nitrogen in the soil, which can benefit other plants. Some popular companions for beans include corn, squash, and cucumbers. These plants can be grown together in a polyculture, providing mutual benefits and creating a diverse and resilient garden ecosystem.
The Three Sisters
The Three Sisters is a traditional companion planting method that involves growing beans, corn, and squash together. The corn provides a structure for the beans to climb, while the beans fix nitrogen in the soil, benefiting the corn and squash. The squash spreads its large leaves to shade the soil, preventing weeds and retaining moisture. This polyculture is a great example of how different plants can work together to create a thriving and diverse garden ecosystem.
Hydroponic Systems

Hydroponic systems provide a controlled environment for growing beans, with precise control over nutrient levels, pH, and water. This method is ideal for indoor growing, where space is limited, and can be used to grow a wide range of crops, including beans. To grow beans hydroponically, use a nutrient-rich solution specifically formulated for hydroponic systems, and provide the plants with a trellis or other support system. With proper care, beans can thrive in hydroponic systems and be ready to harvest in as little as 50 days.
What is the ideal temperature for growing beans?
+The ideal temperature for growing beans is between 60-85°F (15-30°C). Beans can germinate at temperatures as low as 50°F (10°C), but optimal growth occurs when the temperature is above 60°F (15°C).
How often should I water my bean plants?
+Bean plants should be watered consistently, but not excessively. The soil should be kept moist, but not waterlogged. Aim to provide about 1-2 inches of water per week, either from rainfall or irrigation.
Can I grow beans in containers?
+Yes, beans can be grown in containers. Choose a container that is at least 6-8 inches deep and has drainage holes to prevent waterlogging. Fill the container with a well-draining potting mix, and sow the seeds 1-2 inches deep and 2-3 inches apart.



