The concept of strong acids and bases is a fundamental aspect of chemistry, particularly in the realm of acid-base chemistry. Strong acids and bases are characterized by their ability to completely dissociate in water, resulting in a high concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) or hydroxide ions (OH-). This complete dissociation is a key factor in determining the strength of an acid or base. In this article, we will delve into the world of strong acids and bases, exploring their definition, properties, and examples, as well as their importance in various chemical reactions and industrial applications.
Definition and Properties of Strong Acids and Bases

A strong acid is defined as an acid that completely dissociates in water, resulting in a high concentration of hydrogen ions (H+). This complete dissociation is often represented by the equation HA → H+ + A-, where HA is the acid and A- is the conjugate base. Strong bases, on the other hand, are defined as bases that completely dissociate in water, resulting in a high concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-). The dissociation of a strong base is often represented by the equation BOH → B+ + OH-, where BOH is the base and B+ is the conjugate acid.
Examples of Strong Acids and Bases
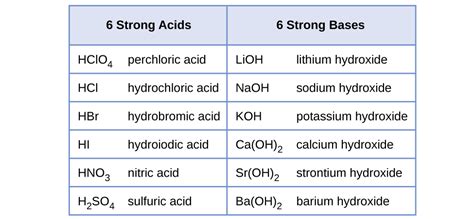
There are several examples of strong acids and bases, including hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), nitric acid (HNO3), and acetic acid (CH3COOH) are not strong acids, but hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), and nitric acid (HNO3) are. On the other hand, some common strong bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2). These strong acids and bases are widely used in various industrial and laboratory applications, such as in the manufacture of fertilizers, dyes, and pharmaceuticals.
| Strong Acid/Bases | Chemical Formula | Dissociation Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrochloric Acid | HCl | HCl → H+ + Cl- |
| Sulfuric Acid | H2SO4 | H2SO4 → 2H+ + SO42- |
| Nitric Acid | HNO3 | HNO3 → H+ + NO3- |
| Sodium Hydroxide | NaOH | NaOH → Na+ + OH- |
| Potassium Hydroxide | KOH | KOH → K+ + OH- |

Importance of Strong Acids and Bases in Chemical Reactions

Strong acids and bases play a crucial role in various chemical reactions, including neutralization reactions, precipitation reactions, and oxidation-reduction reactions. In neutralization reactions, strong acids and bases react with each other to form a salt and water. For example, the reaction between hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) produces sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H2O). This reaction is often represented by the equation HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O.
Applications of Strong Acids and Bases in Industry
Strong acids and bases have numerous applications in various industries, including the manufacture of fertilizers, dyes, and pharmaceuticals. Hydrochloric acid (HCl), for example, is used in the production of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), while sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is used in the production of fertilizers and explosives. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), on the other hand, is used in the production of paper, textiles, and soaps.
Key Points
- Strong acids and bases are characterized by their ability to completely dissociate in water.
- Examples of strong acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), and nitric acid (HNO3).
- Examples of strong bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2).
- Strong acids and bases play a crucial role in various chemical reactions, including neutralization reactions, precipitation reactions, and oxidation-reduction reactions.
- Strong acids and bases have numerous applications in various industries, including the manufacture of fertilizers, dyes, and pharmaceuticals.
In conclusion, strong acids and bases are essential components of chemistry, and their properties and applications are widely used in various industrial and laboratory settings. Understanding the definition, properties, and examples of strong acids and bases is crucial for appreciating their importance in chemical reactions and industrial applications.
What is the difference between a strong acid and a weak acid?
+A strong acid is an acid that completely dissociates in water, resulting in a high concentration of hydrogen ions (H+). A weak acid, on the other hand, is an acid that only partially dissociates in water, resulting in a lower concentration of hydrogen ions (H+).
What are some examples of strong bases?
+Some examples of strong bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2). These strong bases are widely used in various industrial and laboratory applications.
What is the importance of strong acids and bases in chemical reactions?
+Strong acids and bases play a crucial role in various chemical reactions, including neutralization reactions, precipitation reactions, and oxidation-reduction reactions. They are essential components of chemistry, and their properties and applications are widely used in various industrial and laboratory settings.