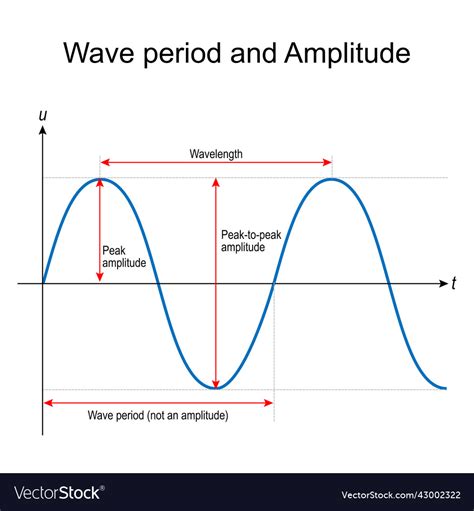
When discussing ocean waves, one of the fundamental parameters that characterize their behavior is the wave period. The wave period, denoted by the symbol T, is the time it takes for one complete wave cycle to pass a given point. In other words, it is the time interval between two consecutive wave crests or troughs. Understanding wave period is crucial in various fields, including oceanography, coastal engineering, and meteorology, as it plays a significant role in determining the energy and impact of waves on coastlines and marine structures.
The importance of wave period lies in its relationship with other wave parameters, such as wave length, wave height, and wave speed. For instance, the wave length (L) is directly related to the wave period through the dispersion relation, which, for deep water waves, is given by L = 1.56T^2. This relationship indicates that longer wave periods correspond to longer wave lengths. Furthermore, the wave period influences the wave's energy, with longer periods generally associated with higher energy waves. This is because the energy of a wave is proportional to the square of its height and the period of the wave.
Key Points
- The wave period (T) is the time taken for one complete wave cycle to pass a given point.
- It is a critical parameter in understanding wave behavior and its impact on coastlines and marine structures.
- The wave period is related to other wave parameters such as wave length, height, and speed through various equations.
- Longer wave periods generally correspond to higher energy waves, which can have significant effects on coastal erosion and marine construction.
- Understanding wave period is essential for predicting wave conditions and for the design of coastal defenses and offshore structures.
Wave Period and Its Relationship with Other Wave Parameters

The relationship between wave period and other wave parameters is governed by physical laws, particularly in the context of deep water waves where the water depth is greater than half the wave length. In such conditions, waves can be considered as deep water waves, and their behavior is relatively well understood. The dispersion relation for deep water waves, L = 1.56T^2, implies that waves with longer periods will have longer lengths and, consequently, higher speeds since wave speed © in deep water is given by c = L/T, which simplifies to c = 1.56T for deep water waves.
Practical Applications of Wave Period Understanding
Understanding wave period has numerous practical applications. In coastal engineering, for example, knowing the expected wave periods at a given location is crucial for designing seawalls, breakwaters, and other coastal defense structures. These structures need to be able to withstand the forces exerted by waves, which are directly influenced by the wave period. Longer period waves, with their higher energies, require more robust structures to prevent damage or failure.
| Wave Parameter | Relationship with Wave Period |
|---|---|
| Wave Length (L) | L = 1.56T^2 (for deep water waves) |
| Wave Speed (c) | c = L/T = 1.56T (for deep water waves) |
| Wave Energy | Proportional to T and the square of wave height |
Measuring Wave Period

Measuring wave period is typically done using instruments such as buoys, which can record the elevation of the sea surface over time. By analyzing the time series data from these measurements, the wave period can be calculated. Satellite altimetry is another method used to measure wave parameters, including wave period, although its application is more limited in coastal areas due to resolution constraints. Understanding how wave period is measured is essential for assessing the accuracy and reliability of wave data, which are critical for various applications, including weather forecasting, coastal engineering, and climate research.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the advancements in understanding and measuring wave period, there are still challenges to be addressed. One of the significant challenges is accurately predicting wave conditions over long periods, which is essential for climate change research and coastal management. Improving predictive models and incorporating new data sources, such as those from satellite missions and advanced buoys, will be crucial for overcoming these challenges. Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques into wave forecasting models is expected to enhance their accuracy and reliability.
What is the significance of wave period in oceanography?
+The wave period is significant because it influences the energy and behavior of waves, which in turn affect coastal erosion, marine life, and the design of coastal defenses and offshore structures.
How is wave period measured?
+Wave period is typically measured using buoys that record the sea surface elevation over time or through satellite altimetry, although the latter has limitations in coastal areas.
What are the practical applications of understanding wave period?
+Understanding wave period is crucial for coastal engineering, marine biology, and meteorology. It helps in designing seawalls, breakwaters, and predicting wave conditions, which are essential for coastal management and climate research.
In conclusion, the wave period is a fundamental parameter in understanding wave behavior and its impacts on coastlines and marine structures. Its relationship with other wave parameters and its practical applications highlight its importance in various fields. As research and technology continue to advance, improving our understanding and predictive capabilities of wave period will be essential for addressing the challenges posed by climate change and for the sustainable management of coastal resources.