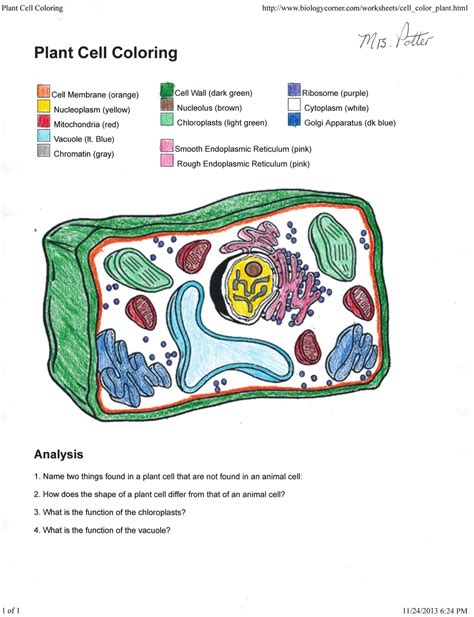
Learning about plant cells can be a fascinating experience, especially when it comes to understanding the intricate details of their structure and function. One of the most engaging ways to study plant cells is through coloring activities, which not only help in memorizing the different components but also make the learning process more enjoyable and interactive. For those looking to create detailed and accurate plant cell diagrams, here are some valuable tips to ensure your coloring is both informative and aesthetically pleasing.
Key Points
- Understand the basic structure of a plant cell, including the cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, and various organelles.
- Choose a color scheme that differentiates between the cell components clearly, making it easier to distinguish between them.
- Pay attention to the proportions and relative sizes of the cell components to maintain anatomical accuracy.
- Label each component clearly, ensuring that the labels are legible and correspond to the correct colors used.
- Consider adding a key or legend to explain the color coding used in the diagram, enhancing its clarity and usability.
Understanding Plant Cell Structure

A plant cell, unlike an animal cell, is enclosed by a rigid cell wall that provides structural support and protection. The cell wall is primarily composed of cellulose, a type of carbohydrate that gives plants their rigidity. When coloring a plant cell, it’s essential to depict the cell wall as the outermost layer, clearly distinguishable from the rest of the cell components. A brown or green color can effectively represent the cell wall, signifying its organic and plant-based composition.
Color Coding for Clarity
A well-chosen color scheme is crucial for creating a clear and informative plant cell diagram. Each component of the cell should be assigned a unique color to prevent confusion and ensure that all parts are easily identifiable. For instance, the nucleus, which houses the cell’s genetic material, can be colored purple or blue to signify its importance and differentiate it from other organelles. The cytoplasm, the jelly-like substance where many metabolic processes occur, can be represented by a light blue or pale yellow color, indicating its fluid and dynamic nature.
| Cell Component | Suggested Color |
|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Brown or Green |
| Nucleus | Purple or Blue |
| Cytoplasm | Light Blue or Pale Yellow |
| Chloroplasts | Green |
| Mitochondria | Red or Orange |

Proportions and Labeling
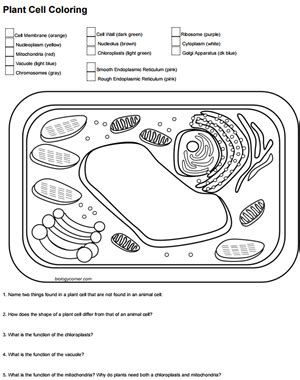
Maintaining the correct proportions of the cell components is vital for an accurate representation. The nucleus, for instance, is typically smaller compared to the cell’s overall size but larger than most other organelles. Ensuring that each component is proportional helps in creating a realistic and educational diagram. Labeling each part clearly is also essential, as it allows viewers to understand the function and importance of each organelle without confusion. Labels should be concise, legible, and placed near the corresponding colored component.
Adding a Key or Legend
To further enhance the clarity and usability of the plant cell diagram, consider adding a key or legend. This key should explain the color coding used for each component, providing a quick reference for viewers. By including a legend, the diagram becomes more self-explanatory, allowing learners to focus on understanding the cell’s structure and function rather than deciphering the colors used.
Why is coloring important in learning about plant cells?
+Coloring is important because it makes learning about plant cells more engaging and interactive. It helps in memorizing the different components of the cell and their functions, making the learning process more enjoyable and effective.
How do I choose the right colors for my plant cell diagram?
+Choose colors that are naturally associated with the function or composition of each cell component. For example, green for chloroplasts and brown for the cell wall. Ensure that each component has a unique color to avoid confusion.
What is the importance of labeling in a plant cell diagram?
+Labeling is crucial as it identifies each component of the cell, making it easier for viewers to understand the diagram. Labels should be clear, concise, and placed near the corresponding component.
By following these tips and considering the importance of accuracy, clarity, and aesthetics, creating a detailed and informative plant cell diagram can be a rewarding experience. Whether for educational purposes or personal interest, the process of coloring and learning about plant cells can deepen one’s understanding of the intricate and fascinating world of cellular biology.
Related Terms:
- Plant cell coloring answers
- Plant cell coloring worksheet
- Animal cell Coloring
- Plant cell coloring pdf
- Biology corner plant cell Coloring
- Plant cell coloring labeled