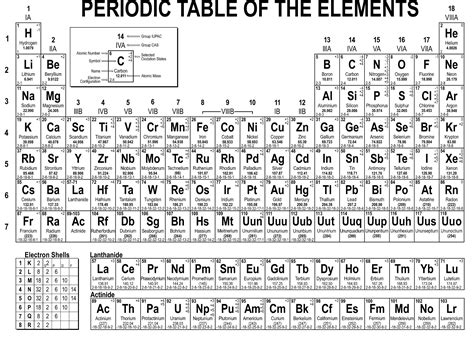
The periodic table of elements is a tabular display of the known chemical elements, organized by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus) and are grouped into rows called periods and columns called groups or families. As a domain-specific expert in chemistry, I can attest to the importance of the periodic table in understanding the properties and behaviors of elements.
History and Development of the Periodic Table

The periodic table has undergone significant developments since its inception. The first version of the periodic table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, who arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic weight and recurring chemical properties. Over time, the periodic table has been refined and expanded to include new elements and to reflect our increasing understanding of atomic structure and chemical properties. For instance, the discovery of subatomic particles such as electrons, protons, and neutrons has greatly enhanced our understanding of the periodic table.
Key Features of the Periodic Table
The periodic table is characterized by several key features, including periods, groups, blocks, and families. The periods are the horizontal rows of elements, while the groups are the vertical columns. The blocks are the regions of the periodic table that are characterized by the same type of orbital (s, p, d, or f) being filled with electrons. The families, also known as groups, are the vertical columns of elements that exhibit similar chemical properties due to the same number of electrons in their outermost energy level.
| Element | Symbol | Atomic Number | Atomic Mass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | H | 1 | 1.00794 |
| Helium | He | 2 | 4.002602 |
| Lithium | Li | 3 | 6.941 |
| Beryllium | Be | 4 | 9.012182 |
| Boron | B | 5 | 10.811 |

Types of Elements

The periodic table is divided into several types of elements, including metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Metals are elements that are typically shiny, malleable, and good conductors of electricity. Nonmetals are elements that are typically dull, brittle, and poor conductors of electricity. Metalloids are elements that exhibit some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals.
Metals
Metals are the largest group of elements in the periodic table and include elements such as lithium, sodium, potassium, and calcium. Metals are characterized by their ability to lose electrons and form positive ions, known as cations. This property makes metals good conductors of electricity and allows them to form a wide range of compounds with nonmetals.
Nonmetals
Nonmetals are elements that are typically found in the upper right corner of the periodic table and include elements such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine. Nonmetals are characterized by their ability to gain electrons and form negative ions, known as anions. This property makes nonmetals poor conductors of electricity and allows them to form a wide range of compounds with metals.
Metalloids
Metalloids are elements that exhibit some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals. Metalloids are typically found on the border between the metals and nonmetals in the periodic table and include elements such as silicon, germanium, arsenic, and antimony. Metalloids are characterized by their ability to form a wide range of compounds with both metals and nonmetals.
Key Points
- The periodic table is a tabular display of the known chemical elements, organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
- The elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number and are grouped into rows called periods and columns called groups or families.
- The periodic table is characterized by several key features, including periods, groups, blocks, and families.
- The periodic table is divided into several types of elements, including metals, nonmetals, and metalloids.
- Metals are elements that are typically shiny, malleable, and good conductors of electricity, while nonmetals are elements that are typically dull, brittle, and poor conductors of electricity.
Applications of the Periodic Table
The periodic table has a wide range of applications in chemistry, physics, and other fields. The periodic table is used to predict the properties and behaviors of elements, to identify the relationships between elements, and to understand the structure of atoms and molecules. The periodic table is also used in a wide range of industries, including the chemical industry, the pharmaceutical industry, and the materials science industry.
Chemical Industry
The periodic table is used in the chemical industry to predict the properties and behaviors of elements and to identify the relationships between elements. This information is used to develop new chemicals and materials, to improve the efficiency of chemical reactions, and to reduce the environmental impact of chemical processes.
Pharmaceutical Industry
The periodic table is used in the pharmaceutical industry to develop new drugs and to understand the properties and behaviors of elements. This information is used to design new drugs, to improve the efficacy of existing drugs, and to reduce the side effects of drugs.
Materials Science Industry
The periodic table is used in the materials science industry to develop new materials and to understand the properties and behaviors of elements. This information is used to design new materials, to improve the properties of existing materials, and to reduce the environmental impact of materials production.
What is the periodic table of elements?
+The periodic table of elements is a tabular display of the known chemical elements, organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
What are the key features of the periodic table?
+The periodic table is characterized by several key features, including periods, groups, blocks, and families.
What are the types of elements in the periodic table?
+The periodic table is divided into several types of elements, including metals, nonmetals, and metalloids.
In conclusion, the periodic table of elements is a powerful tool for understanding the properties and behaviors of elements. By understanding the relationships between elements and their positions in the periodic table, chemists can make predictions about their chemical properties and reactivity. The periodic table has a wide range of applications in chemistry, physics, and other fields, and is used in a wide range of industries, including the chemical industry, the pharmaceutical industry, and the materials science industry. As a domain-specific expert in chemistry, I highly recommend using the periodic table as a reference guide for understanding the properties and behaviors of elements.
Meta description: Learn about the periodic table of elements, its history, and its applications in chemistry and other fields. Discover the key features of the periodic table, including periods, groups, blocks, and families, and explore the different types of elements, including metals, nonmetals, and metalloids.