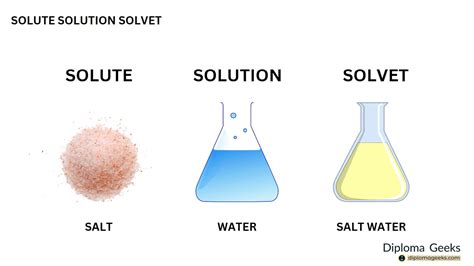
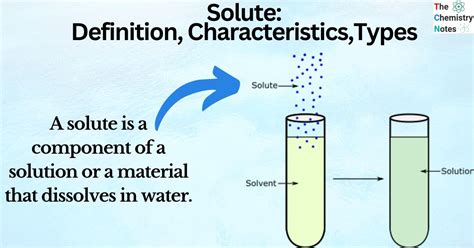
The term "solute" is a fundamental concept in biology and chemistry, referring to a substance that is dissolved in a solvent, forming a solution. In the context of biology, solutes play a crucial role in various physiological processes, including cellular transport, metabolic pathways, and maintaining homeostasis. A solute can be a solid, liquid, or gas that is dissolved in a liquid solvent, such as water, to form a homogeneous mixture. The solute can be either organic or inorganic in nature, and its properties, such as molecular weight, charge, and polarity, determine its interaction with the solvent and its biological function.
In biological systems, solutes are essential for maintaining proper cellular function, regulating osmotic balance, and facilitating the transport of nutrients and waste products. For example, glucose, amino acids, and ions such as sodium and potassium are solutes that are vital for cellular metabolism, energy production, and maintaining proper ion balance. The concentration of solutes in a solution can affect the rate of biological processes, such as enzyme activity, protein folding, and membrane transport. Understanding the behavior of solutes in biological systems is essential for grasping various biological phenomena, including osmosis, diffusion, and active transport.
Key Points
- A solute is a substance that is dissolved in a solvent, forming a solution.
- Solutes play a crucial role in various physiological processes, including cellular transport and metabolic pathways.
- The properties of a solute, such as molecular weight and charge, determine its interaction with the solvent and its biological function.
- The concentration of solutes in a solution can affect the rate of biological processes.
- Understanding the behavior of solutes in biological systems is essential for grasping various biological phenomena, including osmosis and diffusion.
Types of Solutes in Biological Systems
Biological systems contain a wide range of solutes, including ions, sugars, amino acids, and other organic compounds. Ions, such as sodium, potassium, and chloride, are essential for maintaining proper ion balance and regulating various physiological processes, including nerve and muscle function. Sugars, such as glucose and fructose, are vital for energy production and can be found in various biological fluids, including blood and urine. Amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, are also solutes that play a crucial role in protein synthesis and other biological processes.
Properties of Solutes
The properties of solutes, such as molecular weight, charge, and polarity, determine their interaction with the solvent and their biological function. For example, the molecular weight of a solute can affect its rate of diffusion and transport across biological membranes. The charge of a solute can also influence its interaction with other molecules, such as proteins and lipids, and affect its biological activity. The polarity of a solute can determine its solubility in a particular solvent and its ability to interact with other polar molecules.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | Affects rate of diffusion and transport across biological membranes |
| Charge | Influences interaction with other molecules and affects biological activity |
| Polarity | Determines solubility in a particular solvent and ability to interact with other polar molecules |
Biological Importance of Solutes

Solutes play a vital role in various biological processes, including cellular transport, metabolic pathways, and maintaining homeostasis. The concentration of solutes in a solution can affect the rate of biological processes, such as enzyme activity, protein folding, and membrane transport. For example, the concentration of glucose in the blood can affect the rate of glycolysis, a metabolic pathway that converts glucose into energy. The concentration of ions, such as sodium and potassium, can also affect the rate of nerve and muscle function.
In addition to their role in biological processes, solutes also play a crucial role in maintaining proper osmotic balance. Osmotic balance refers to the balance of solutes and water across biological membranes, which is essential for maintaining proper cellular function. An imbalance of solutes can lead to various biological disorders, including dehydration, edema, and electrolyte imbalances.
Methods for Analyzing Solutes
Various methods can be used to analyze solutes in biological systems, including spectroscopy, chromatography, and electrophoresis. Spectroscopy involves the use of light to analyze the properties of solutes, such as their molecular weight and charge. Chromatography involves the use of a stationary phase and a mobile phase to separate and analyze solutes based on their properties, such as molecular weight and polarity. Electrophoresis involves the use of an electric field to separate and analyze solutes based on their charge and size.
What is a solute in biology?
+A solute is a substance that is dissolved in a solvent, forming a solution. In biology, solutes play a crucial role in various physiological processes, including cellular transport and metabolic pathways.
What are the properties of solutes that affect their biological function?
+The properties of solutes, such as molecular weight, charge, and polarity, determine their interaction with the solvent and their biological function. These properties can affect the rate of diffusion and transport across biological membranes, as well as the interaction with other molecules.
How do solutes affect biological processes?
+Solutes can affect the rate of biological processes, such as enzyme activity, protein folding, and membrane transport. The concentration of solutes in a solution can also affect the rate of metabolic pathways and the maintenance of proper osmotic balance.
In conclusion, solutes play a vital role in various biological processes, including cellular transport, metabolic pathways, and maintaining homeostasis. Understanding the properties of solutes, such as molecular weight, charge, and polarity, is essential for predicting their behavior in biological systems and grasping their biological function. By analyzing the concentration of solutes in a solution and their interaction with other molecules, researchers can gain insights into their potential role in various biological processes and disorders.