A pump is a device that uses mechanical or electrical energy to move fluids, such as liquids or gases, from one location to another. Pumps are widely used in various industries, including water supply, oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation, among others. The primary function of a pump is to create a pressure difference between two points, allowing the fluid to flow from an area of low pressure to an area of high pressure. This is achieved through the conversion of mechanical or electrical energy into hydraulic energy, which is then transferred to the fluid.
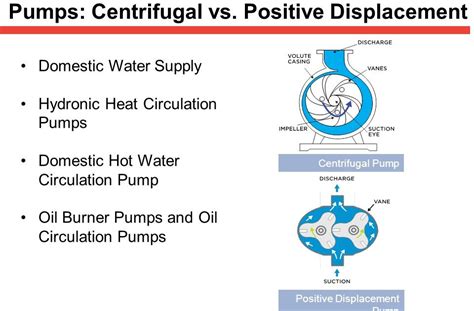
Pumps can be classified into several types based on their operating principle, including centrifugal pumps, positive displacement pumps, and rotary pumps. Centrifugal pumps, for example, use a spinning impeller to create a pressure difference, while positive displacement pumps use a piston or diaphragm to displace a fixed volume of fluid. Rotary pumps, on the other hand, use a rotating element to create a pressure difference. Each type of pump has its own unique characteristics and is suited for specific applications.
Key Points
- A pump is a device that uses energy to move fluids from one location to another
- Pumps are used in various industries, including water supply, oil and gas, and power generation
- The primary function of a pump is to create a pressure difference between two points
- Pumps can be classified into several types, including centrifugal, positive displacement, and rotary pumps
- Each type of pump has its own unique characteristics and is suited for specific applications
Types of Pumps

Centrifugal pumps are one of the most common types of pumps used in various industries. They operate by using a spinning impeller to create a pressure difference, which then drives the fluid through the pump. Centrifugal pumps are suitable for high-flow, low-pressure applications and are often used in water supply systems, irrigation systems, and HVAC systems.
Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive displacement pumps, on the other hand, use a piston or diaphragm to displace a fixed volume of fluid. They operate by creating a pressure difference between the inlet and outlet of the pump, which then drives the fluid through the pump. Positive displacement pumps are suitable for low-flow, high-pressure applications and are often used in chemical processing, oil and gas, and power generation.
| Type of Pump | Description |
|---|---|
| Centrifugal Pump | Uses a spinning impeller to create a pressure difference |
| Positive Displacement Pump | Uses a piston or diaphragm to displace a fixed volume of fluid |
| Rotary Pump | Uses a rotating element to create a pressure difference |

Pump Applications
Pumps have a wide range of applications in various industries. In the water supply industry, pumps are used to distribute water from treatment plants to households and businesses. In the oil and gas industry, pumps are used to extract oil and gas from wells and transport them to refineries. In the power generation industry, pumps are used to circulate coolant through nuclear reactors and to feed water into steam turbines.
Pump Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the efficient and reliable operation of pumps. This includes tasks such as checking and replacing worn-out parts, cleaning and lubricating moving parts, and monitoring pump performance. Proper maintenance can help extend the lifespan of pumps, reduce energy consumption, and prevent costly repairs.
What is the primary function of a pump?
+The primary function of a pump is to create a pressure difference between two points, allowing the fluid to flow from an area of low pressure to an area of high pressure.
What are the different types of pumps?
+Pumps can be classified into several types, including centrifugal pumps, positive displacement pumps, and rotary pumps.
What is the importance of regular pump maintenance?
+Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the efficient and reliable operation of pumps. It can help extend the lifespan of pumps, reduce energy consumption, and prevent costly repairs.



