Reinsurance is a vital component of the insurance industry, allowing companies to manage risk and protect their financial stability. As a complex and nuanced field, reinsurance requires a deep understanding of the underlying principles and mechanisms that drive its operations. In this article, we will delve into the world of reinsurance, providing expert insights and actionable tips for those seeking to navigate this intricate landscape. Whether you are an insurance professional, a risk manager, or simply an interested observer, this discussion is designed to offer valuable perspectives and practical advice on the art of reinsurance.
Key Points
- Understand the fundamentals of reinsurance, including types, structures, and mechanisms.
- Conduct thorough risk assessments to identify areas where reinsurance can provide optimal protection.
- Develop a comprehensive reinsurance strategy that aligns with your company's overall risk management goals.
- Monitor and adjust your reinsurance program regularly to ensure it remains effective and efficient.
- Consider seeking the advice of a reinsurance expert or broker to help navigate the complex reinsurance market.
Understanding Reinsurance Fundamentals

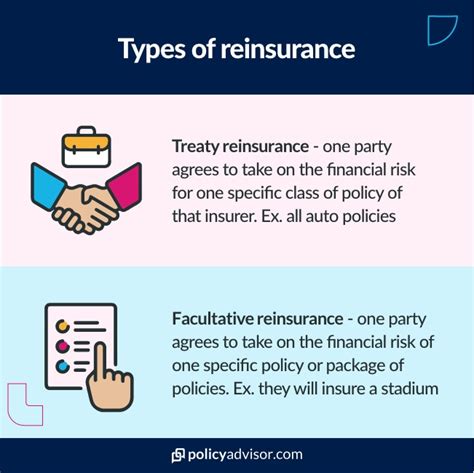
At its core, reinsurance is the process by which an insurance company transfers some of its risk to another insurance company, known as the reinsurer. This transfer of risk allows the original insurer to reduce its potential losses and stabilize its financial position. There are several types of reinsurance, including treaty reinsurance, which involves the transfer of a large portion of an insurer’s risk, and facultative reinsurance, which involves the transfer of a single, specific risk. Understanding these fundamental concepts is essential for developing an effective reinsurance strategy.
Types of Reinsurance
There are several types of reinsurance, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. Treaty reinsurance, for example, provides broad coverage for an insurer’s entire portfolio, while facultative reinsurance offers more targeted protection for specific risks. Other types of reinsurance include excess of loss reinsurance, which provides coverage for losses that exceed a certain threshold, and quota share reinsurance, which involves the transfer of a fixed percentage of an insurer’s risk. By understanding the different types of reinsurance available, companies can select the best option for their specific needs and risk profiles.
| Reinsurance Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Treaty Reinsurance | Transfer of a large portion of an insurer's risk |
| Facultative Reinsurance | Transfer of a single, specific risk |
| Excess of Loss Reinsurance | Coverage for losses that exceed a certain threshold |
| Quota Share Reinsurance | Transfer of a fixed percentage of an insurer's risk |

Developing a Comprehensive Reinsurance Strategy

A well-designed reinsurance strategy is essential for maximizing the benefits of reinsurance and minimizing its costs. This involves conducting thorough risk assessments, identifying areas where reinsurance can provide optimal protection, and selecting the most appropriate reinsurance type and structure. Companies should also consider their overall risk management goals and objectives, as well as their financial position and capacity for risk retention. By taking a comprehensive and integrated approach to reinsurance, companies can ensure that their reinsurance program is aligned with their broader business strategy and risk management objectives.
Risk Assessment and Management
Risk assessment and management are critical components of a comprehensive reinsurance strategy. This involves identifying potential risks, assessing their likelihood and potential impact, and developing strategies for mitigating or transferring those risks. Companies should also consider their risk tolerance and capacity for risk retention, as well as their ability to absorb potential losses. By taking a proactive and informed approach to risk management, companies can minimize their exposure to potential losses and maximize the benefits of reinsurance.
What is the primary purpose of reinsurance?
+The primary purpose of reinsurance is to allow insurance companies to manage risk and protect their financial stability by transferring some of their risk to another insurance company.
What are the different types of reinsurance?
+There are several types of reinsurance, including treaty reinsurance, facultative reinsurance, excess of loss reinsurance, and quota share reinsurance.
How do I develop a comprehensive reinsurance strategy?
+To develop a comprehensive reinsurance strategy, you should conduct thorough risk assessments, identify areas where reinsurance can provide optimal protection, and select the most appropriate reinsurance type and structure.
In conclusion, reinsurance is a complex and multifaceted field that requires a deep understanding of its underlying principles and mechanisms. By following the 5 reinsurance tips outlined in this article, companies can develop a comprehensive reinsurance strategy that aligns with their overall risk management goals and objectives. Whether you are an insurance professional, a risk manager, or simply an interested observer, this discussion is designed to offer valuable perspectives and practical advice on the art of reinsurance.